A fibula fracture is a break of the fibula bone in the lower leg. It is either a sudden onset acute fracture or a gradual onset stress fracture.
A fibula fracture can occur at the same time as a tibia fracture. Or they can occur on their own in isolation. If you suspect a lower leg fracture seek medical attention immediately.
Combined tibia & fibula fracture symptoms
- Fractures of both the tibia and fibula bones in the lower leg will usually be fairly obvious.
- Severe pain usually following an impact, collision, or fall is accompanied by rapid swelling.
- Weight-bearing will be impossible and the lower leg may be deformed.
Isolated fibula fracture symptoms
A fibula fracture where there is no fracture of the tibia can also occur from landing on a twisted foot. Or it can also result from a direct impact on the lower leg. However, pain in the calf area is likely to be a lot less than a combined tibia-fibula fracture.
- Depending on the severity of the injury, the patient may only complain of tenderness over the area of the fracture.
- The athlete will most likely limp or be unable to bear weight on the fractured leg.
- In more severe cases there will be deformity where bones have been displaced.
Stress fracture symptoms
Symptoms of a fibula stress fracture include:
- A gradual build-up of pain on the outside of the lower leg which eases with rest and increases with activity.
- Tenderness over the point of the fracture.
- Aching or throbbing pain at night. See fibula stress fracture for more detailed information.
Fibula fracture
They are usually caused by landing on a twisted foot, or from direct impact or trauma.
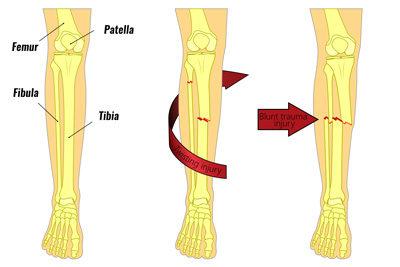
The fibula is the smaller of the two shin bones on the outside of the lower leg. The bony lump on the outside of the ankle is called the lateral malleolus. This is part of the fibula bone on the outside of the lower leg.
The function of the fibula is mainly to provide a surface for muscles to attach. The larger tibia bone bears most of the weight.
Maisonneuve injury
A Maisonneuve injury occurs when the membrane connecting the tibia and fibula at the ankle is torn (high ankle sprain), along with a fracture higher up the fibula. This may appear as a simple injury with mild to moderate pain. But the ankle is unstable and requires surgery to stabilize the joint.
Potts fracture
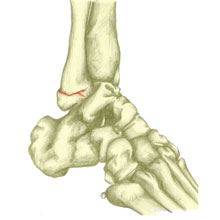
Traumatic fractures of the Fibula can occur with a severe ankle sprain. An avulsion fracture happens when a ligament pulls part of the bone away. A fracture of the bony bit on the outside of the ankle known as the malleolus is called a Pott’s fracture.
Read more on Pott’s fracture.
Stress fracture of the fibula
Stress fractures of the fibula do sometimes occur. However, these are far less common than stress fractures of the tibia. This is because the fibula is not a load-bearing bone. They are more likely to be caused by repetitive muscle traction forces on the bone.
Treatment for an isolated fibula fracture
Assuming the stability of the ankle is not affected then treatment is rest, pain relief medications as required, and the use of crutches.
Once the bone has healed then rehabilitation exercises for the lower leg include stretching, strengthening, proprioception, and sports-specific or functional exercises.
