An ACL sprain (torn ACL) is a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee joint. Our full ACL rehab program takes you step-by-step from initial injury to full fitness.
Medically reviewed by Dr Chaminda Goonetilleke, 21st Dec. 2021
Torn ACL symptoms
In most cases, if you have a torn ACL, you will be aware that something serious has happened. Symptoms include:
- Sudden, acute knee pain
- An audible pop or crack at the time of injury
- Rapid swelling (but not always)
- Knee feels warm to the touch.
- An unstable knee, if you are able to walk
Your physio or doctor uses assessment tests to help diagnose your ACL sprain. These include the Anterior drawer test and Lachman’s test.
An MRI scan confirms the diagnosis. However, an X-ray is only useful for detecting associated bone injuries such as an avulsion fracture. This is where the ligament tears, pulling a small piece of bone away with it.
What is an ACL sprain?
An ACL sprain is a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament in the knee. They are either partial tears or full tears (ruptures) depending on the force of the injury.
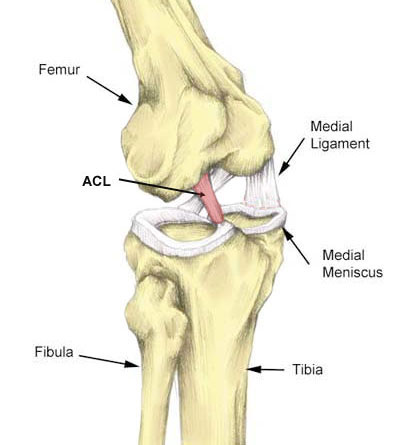
The anterior cruciate ligament runs diagonally across the knee. It originates from the back of the femur (thigh bone) and attaches to the front of the tibia. Its function is to prevent the tibia (shin bone) from moving excessively forwards.
Causes
Injuries to the ACL usually occur as a result of a twisting force in the knee, or if your tibia (shin bone) is forced forwards. Twisting happens when landing after a jump for example. The foot is planted on the ground, whilst the knee twists inwards.
A direct blow to the outside of the knee causes it to buckle inwards. This causes excessive movement of the tibia (shin bone) resulting in damage to other structures within the knee, as well as a torn ACL.
Skiing is also a common cause of ACL sprains. The tips of the skis dig into the snow forcing the tibia forwards.
Treatment for ACL sprains
If you believe that you have a suspected ACL injury or tear, you should seek professional advice as soon as possible. However, it may not be possible to diagnose your ACL sprain until the swelling has gone down.
Immediate first aid involves applying the P.R.I.C.E. therapy principles (protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation) to reduce pain and swelling. Treatment methods include:
- Cold therapy & compression
- Wearing a knee support or brace
- Knee ligament taping
- Rehabilitation exercises
- Surgery (not always required)
